As quoted in Wikipedia: The Internet of things (IoT) describes the network of physical objects—“things”—that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for the purpose of connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems over the Internet. Refer: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_of_things
Internet + Things = IoT
In the IoT system, things can be anything that part of the IoT system capable of sense, transmit, or receive or act upon the information to achieve a common goal.
Hence Things include a microcontroller, sensor, mobile device, cloud service, actuators, etc.
First IoT System:
1990: Considered the first IoT device, John Romkey created a toaster that could be turned on and off over the Internet for the October ’89 INTEROP conference.
The architecture of IoT Systems:
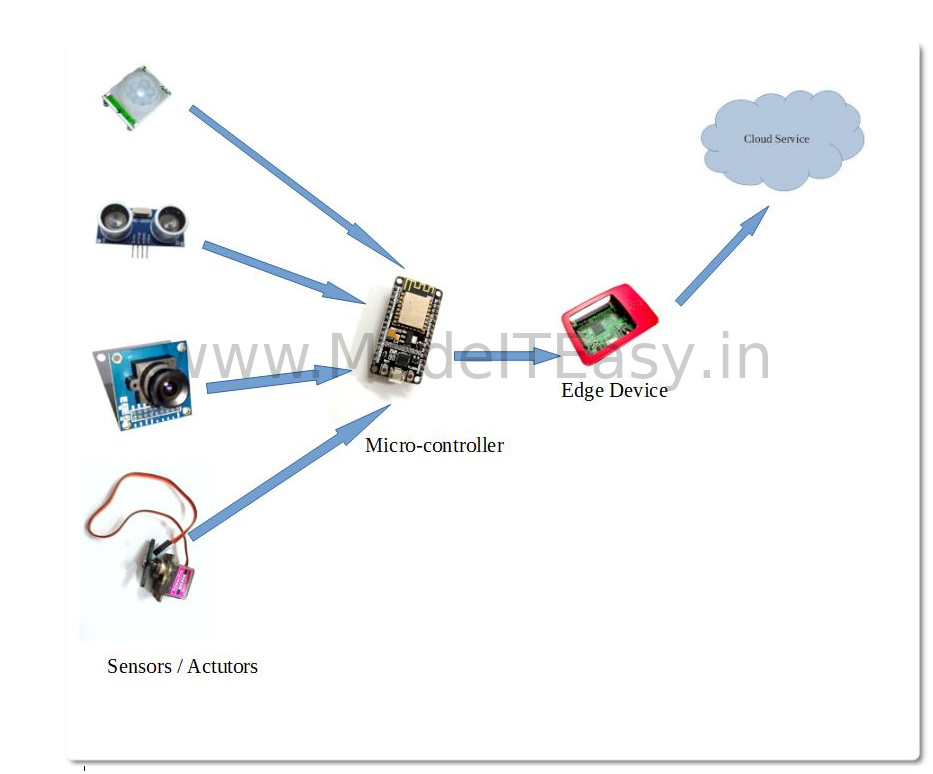
IoT Systems are diverse in nature, so as their architecture. But we can generalize the architecture to fit it to most of the IoT systems. IoT system includes various components as sensors, actuators, micro-controllers, Edge device, and Cloud Service.
Sensors: Sensors are used to collect surrounding information such as temperature, humidity, vibration, motions etc.
Actuators: Actuators are the action components that can perform some action such as servo motors, robotic arm etc.
Micro-controllers: Micro-Controllers are integrated circuits with the mounted processing unit, memory, and I/O connections. Micro-Controllers usually perform logical operations based on the sensor’s data and can also provide commands to actuators to perform certain actions. Micro-controllers are also capable of sending data to cloud services for further processing.
Edge Device: Albeit most of the micro-controllers are capable of accessing the internet and communicate to cloud services, but it’s not preferable as these devices have got low memory and processing capability hence we prefer an intermediary known as an Edge device that receives input from micro-controllers process/ filter it and communicates to cloud-based services for further processing.
Cloud Service: Most of the IoT System is backed up with a Cloud-based Service that store, analyzes and process the data. As an example, if we are developing a Smart-Door system, that would decide to open the door or not based on the picture captured when the bell goes off. When someone rings the bell at the door, the security camera takes the picture of it and via the miro controllers, the cloud service receives the picture and decides (using image processing) whether the door needs to be open or not.